Full window version
(looks a little nicer). Click <Back> button to get back to
small framed version with content indexes.
Definition
To describe how things move we often use the basic quantities of length,
mass, and time. Quantities such as velocity, acceleration, force and energy
are very powerful ones that help us understand how an object's position will
change over time and how it will interact with other things in the universe.
Momentum and its cousin angular momentum are other very powerful
quantities.
Ordinary momentum is a measure of an object's tendency to move at
constant speed along a straight path.
Momentum depends on speed and mass. A train moving at 20 mph has more momentum
than a bicyclist moving at the same speed. A car colliding at 5 mph does not
cause as much damage as that same car colliding at 60 mph. For things moving in
straight lines momentum is simply mass ×
speed. In astronomy most things move in curved paths so we generalize the idea
of momentum and have angular momentum. Angular momentum measures an object's
tendency to continue to spin. An ``object'' can be either a single body or two
or more bodies acting together as a single group.
angular momentum = mass × velocity × distance (from point object is
spinning or orbiting around)
Very often in astronomy, the object (or group of objects) we're observing has
no outside forces acting on it in a way to produce ``torques'' that would disturb
the angular motion of the object (or group of objects). A ``torque'' is
simply a force acting along a line that is off the object's spin axis. In these cases,
we have conservation of angular momentum.
conservation of angular momentum---the total amount of angular momentum does
not change with time no matter how the objects interact with one another.
A planet's velocity and distance from the Sun will change but the
combination of speed×distance will not change unless another
planet or star passes close by and provides an extra gravity force.
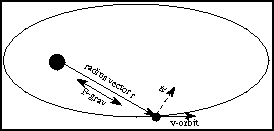
The area swept out by a line connecting an orbiting object and the central point
is the same for any two equal periods of times. That line is called a
radius vector in the following discussion. The rate of
change of the swept-out area does NOT change with time. The line along which
gravity acts is parallel to the radius vector. This means that
there are no torques disturbing the
angular motion and, therefore, angular momentum is conserved. The part of the orbital
velocity (v-orbit) perpendicular (at a right angle) to the radius vector
(r) is vt. The rate of
change of the swept-out area = r×vt/2.
To calculate the orbital angular momentum use vt
for the velocity. So, the angular momentum = mass × vt × r
= mass × 2 × (rate of change of area). That value does not change over time.
So if r decreases, v-orbit (and vt) must increase! If r
increases, v-orbit (and vt) must decrease. This is just what Kepler
observed for the planets!
The total angular momentum = spin angular momentum + orbital angular momentum. The total
angular momentum is CONSTANT. To find the
spin angular momentum, subdivide the object into small pieces of mass and find the
angular momentum for each of the small pieces. Then add up the angular momentum
for all of the pieces. The Earth's spin speed
is decreasing so its spin angular momentum is DEcreasing. Therefore, the Moon's orbital
angular momentum must compensate by INcreasing. It does this by increasing the Earth-Moon
distance.

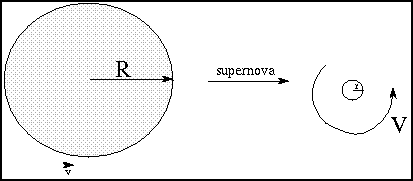
Originally, a big star has a core
10,000's - 100,000's km in radius (the whole star is even bigger!).
Here the radius is used instead of the diameter, because what is
important is how far each piece of the core is from the spin axis that goes
through the exact center.
The core spins at 2 - 10 km/sec at the core's equator. If no external forces produce
torques, the angular momentum is constant. During a supernova the outer layers
are blown off and the core shrinks to only 10 kilometers in radius! The core angular
momentum is approximately = 0.4×M×V×R and the mass M
has stayed approximately the same. When the radius R
shrinks by factors of 10,000's, the spin speed
V must increase by 10,000's of times.
Sometimes the neutron star suddenly
shrinks slightly (by a millimeter or so) and it spins faster. Over time,
though, the neutron star has been producing radiation from its strong magnetic
field. This radiation is produced at the expense of the rotational energy and the
angular momentum is not strictly conserved---it slowly decreases. Therefore, the neutron
star spin speed slowly decreases.
Gas flowing from one star falls toward its compact companion into an orbit around
it. The orbital angular momentum is conserved, so as the gas' distance from the compact
companion DEcreases, its orbital speed must INcrease. It forms a rapidly rotating
disk-like whirlpool called an accretion disk. Over time some of the gas in the
disk gas give torques to other parts of the disk's orbital motions through friction. This
causes their angular momentum to decrease. Some of that gas, then, eventually falls onto
the compact companion.

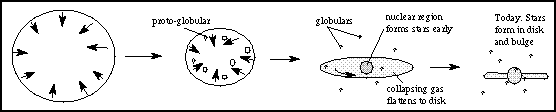
A huge slowly spinning gas cloud collapses. Parts of
the roughly spherical gas cloud break up into small chunks to form stars and
globular clusters. As the rest of the gas cloud collapses, the inner
denser parts collapse more rapidly than the less dense parts. Stars form
in the inner denser parts before they form in the outer less dense parts.
All the time as
the cloud collapses, the spin speed must increase. Since no outside
forces produce torques, the angular momentum is conserved. The rapidly spinning
part of gas cloud eventually forms a disk. This is because the cloud can
collapse more easily in a direction parallel to the spin axis. The gas that
is orbiting perpendicular to the spin axis has enough inertia to
resist the inward pull of gravity (the gas feels a ``centrifugal force''). The
most dense parts of the disk will form stars.
last updated: 19 August 1997
Nick Strobel --
Email:
strobel@lightspeed.net
(805) 395-4526
Bakersfield College
Physical Science Dept.
1801 Panorama Drive
Bakersfield, CA 93305-1219
�